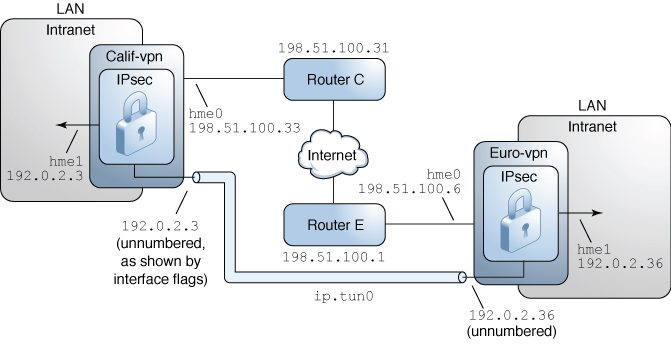
Description of the Network Topology for the IPsec Tasks to Protect a VPN
-
Each system is using an IPv4 address space.
These procedures also work with IPv6 addresses or a combination of IPv4 and IPv6 addresses.
-
Each system has two interfaces. The net0 interface connects to the Internet. In this example, Internet IP addresses begin with 198.51.100. The net1 interface connects to the company's LAN, its intranet. In this example, intranet IP addresses begin with the number 192.0.2.
-
Each system requires ESP encryption with the AES algorithm. The AES algorithm uses a 128-bit or 256-bit key.
-
Each system requires ESP authentication with the SHA-2 algorithm. In this example, the SHA-2 algorithm uses a 512-bit key.
-
Each system can connect to a router that has direct access to the Internet.
-
Each system uses shared security associations.
The procedures in this section assume the following setup. For a depiction of the network, see Sample VPN Between Offices Connected Across the Internet.
The following illustration shows the configuration parameters used in the procedures.
Figure 13 Sample VPN Between Offices Connected Across the Internet
The configuration parameters are listed in the following table.
|
For information about tunnel names, see Administering IP Tunnels in Administering TCP/IP Networks, IPMP, and IP Tunnels in Oracle Solaris 11.3. For information about address objects, see How to Configure an IPv4 Interface in Configuring and Managing Network Components in Oracle Solaris 11.3 and the ipadm(1M) man page.