Indicator Blink Rates
Note - The blink rate information described here might not apply to all server types (for example, blade or rack mount).
This section describes the following indicator blink rates:
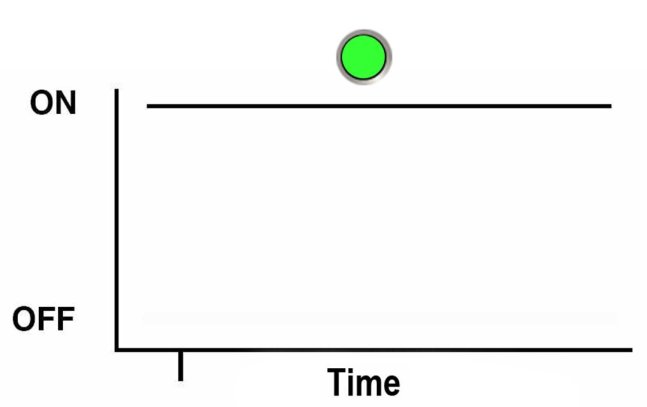
Steady On
For the steady on state, an indicator is continually on (lit) and does not blink. This indicates a continuing condition, for example, an operational state (green) or a Service Action Required fault state (amber).
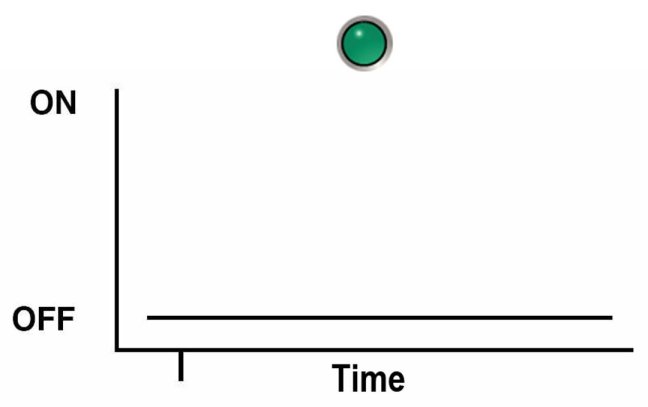
Steady Off
For the steady off state, an indicator is continually off (not lit) and does not blink. This indicates that a system is not operational, for example, no AC power (unlit green system OK indicator) or a subsystem not in a fault state (unlit amber Service Action Required indicator).
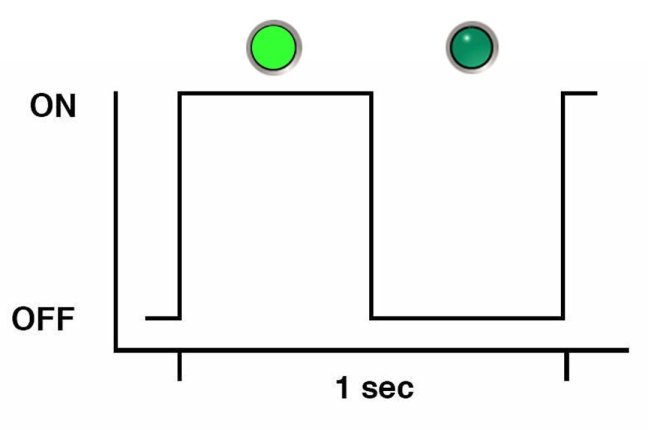
Slow Blink Rate
For the slow blink rate, the indicator (typically green) repeatedly lights for half a second during a one second interval (1 Hz) and turns off for half a second. The slow blink rate indicates an on-going activity. For example, the slow blink rate occurs when a device is rebuilding, booting, or in transition from one mode to another.
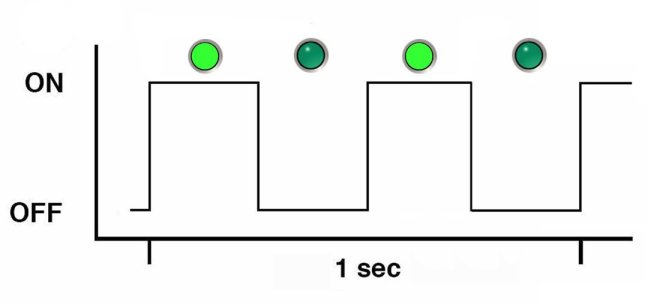
Fast Blink Rate
For the fast blink rate, the indicator repeatedly blinks twice (on, off, on) during a one second interval (2 Hz). The fast blink rate indicates activity or data transfer.
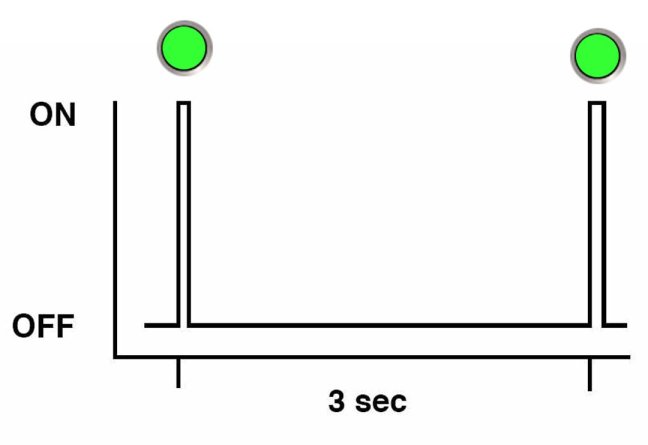
Single (Standby) Blink Rate
For the single blink rate, the indicator repeatedly flashes once at the beginning of a three second interval. This indicates a component or system in standby mode. For example, the single blink rate occurs when a server is in standby power mode or a when hot spare device is waiting to be used (also used with amber indicators to indicate a predicted fault).
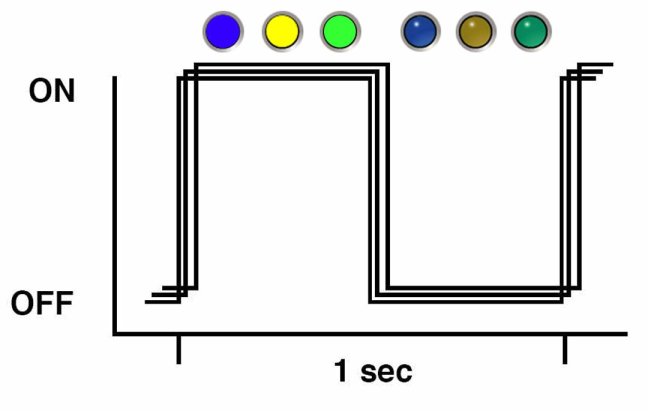
Slow Unison Blink Rate
For the slow unison blink rate, the indicators on the component blink in unison for half a second during a one second interval (1 Hz). Typically, this is limited to three successive blinks. This confirms the successful insertion of a removable device (for example, a storage drive or blade) into a powered system (confirming the power connection).
Insertion Blink
The insertion blink is three successive blinks of a hot-swap component's primary status indicator (for example, the green system OK indicator). The insertion blink occurs immediately after three successive unison blinks (see Slow Unison Blink Rate) of all the component indicators.
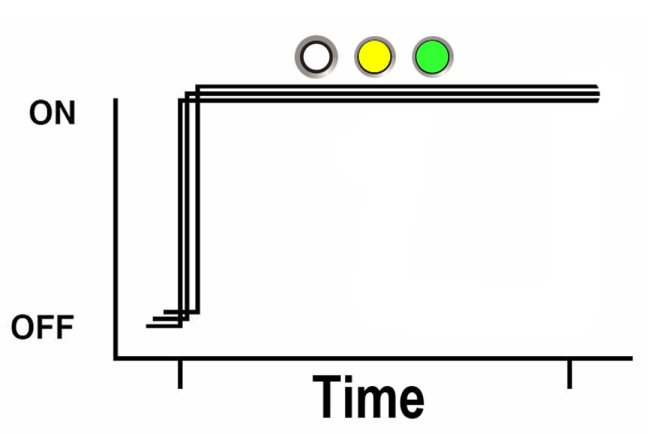
Unison Steady On
For the unison steady on, all indicators are simultaneously on steady (see Steady On). This occurs during the front panel lamp test (see Front Panel Lamp Test).
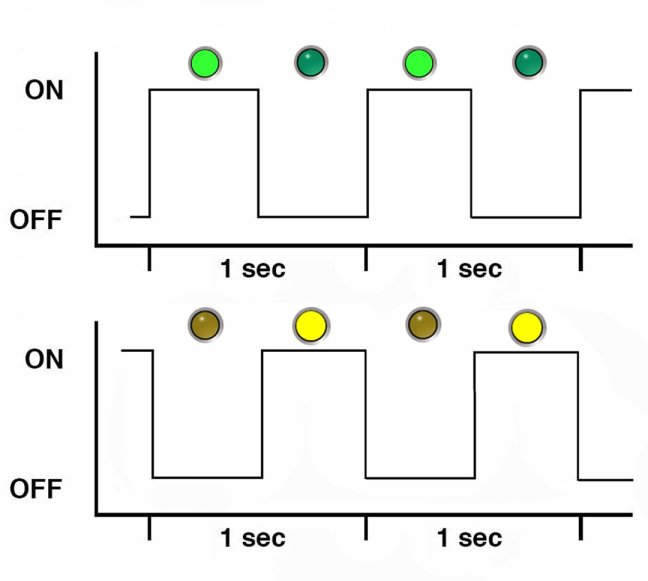
Alternating (Invalid FRU) Blink Rate
A repeating sequence of lit green and amber indicators at 1 Hz. Indicates that a component has an incorrect version or mismatch (for example, a power supply with a lower rating than the one specified). Also used for an unsupported component, a component in an unsupported slot, or a blade (server module) that causes a power supply to be oversubscribed for that system.
Feedback Flash
An indicator flashes on and off during periods of activity, commensurate with the activity, but flashing does not exceed the 2 Hz fast blink rate (see, Fast Blink Rate). For example, disk drive read and write activity and communication port transmit and receive activity.
Data Blink Rate
An indicator that is normally on repeatedly turns off twice during a one-second interval (2 Hz—see also, Fast Blink Rate) while data activity is taking place.
Sequential (Diagnostic) Blink Rate
A repeating sequence in which each indicator successively lights for 0.5 sec each to indicate that diagnostics are running. This blink rate is used only on systems or components capable of running diagnostics (for example, blade servers).