Otherwise elements are used only in forks. If you set up “if” elements for one or more branches in a fork, you can use the Otherwise element as an “else” statement to handle all visitors who do not meet the criteria of the other branches.
Using an Otherwise element is optional, but it is highly recommended. If you do not include this element, site visitors who do not qualify for the other branches do not proceed to the next element in the scenario. However, the system does keep waiting for them to do so, which may have a negative effect on site performance. See Tips for Creating Efficient Scenarios for more information.
The following example shows an Otherwise element:
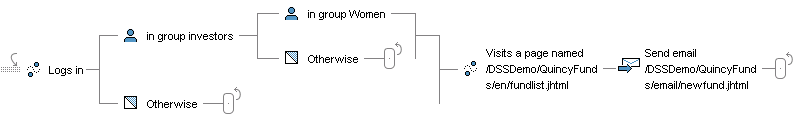
Here, the two Otherwise elements are followed by Stop elements. The effect is as follows: people who log in but are not in the profile group Investors are removed from the scenario. People who are in the group Investors but not in the group Women are also excluded from the scenario.
Note that Otherwise elements are designed to work only in conjunction with Condition or People elements. Do not use them on the branch of a fork whose other branches start with Event elements. In the example above, you could not do the following:
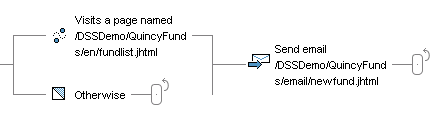
This use of an Otherwise element is invalid. If site visitors reach this stage in the scenario, the system will keep waiting for them to visit the specified page for as long as the scenario is active. It will not apply the Otherwise element to them if, for example, they visit a different page or log out of the site.