Configure a Database Zone
After you create a Database Zone Domain (see Create a Database Zone Domain), you can configure a zone for that domain.
Note - Configuring a zone for an Application Domain using the assistant is not supported.
- Access the SuperCluster Virtual Assistant.
-
In the navigation panel, select Zones.
A list of configured zones and configured SCAN Address Groups appears. These configured zones originate from the I/O Domains tab.
- Click Add to configure a new zone.
-
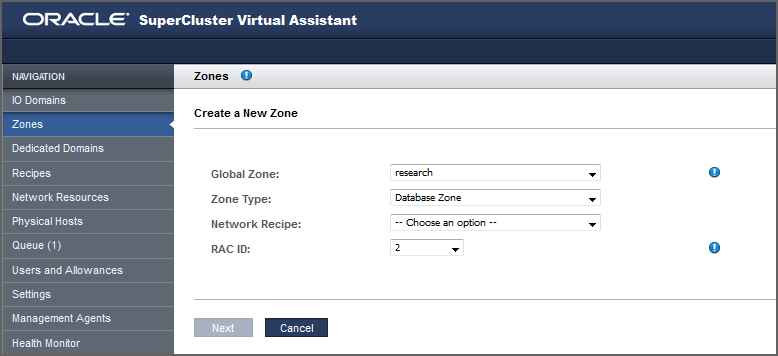
Define these parameters.
-
Global Zone – Choose the domain name from the list of Global Zones.
-
Zone Type – Choose Database Zone.
-
Network Recipe – Select a network recipe:
-
One of the network recipes. See Create a Network Recipe.
-
Custom Network Recipe – Define these parameters:
-
Domain Name – Type the domain name, such as example.com, for this zone.
-
Name Servers – Type a list of comma or space-separated IP addresses of name servers for this zone.
-
Time Servers – Type a list of comma or space-separated IP addresses of time servers for this zone.
-
Time Zone – Choose a time zone for this zone.
-
-
-
RAC ID – If you chose Database Zone as the Zone Type, choose the RAC ID where this zone will belong. An existing RAC ID contains the settings from the initial installation (client networks, network recipes and VLAN tags). Oracle SuperCluster supports a maximum of eight RAC databases.
Caution - If you are configuring an additional zone that will be part of an existing RAC, you must choose the same RAC ID that you used for the other zone.
-
- Click Next.
-
Define these parameters.
-
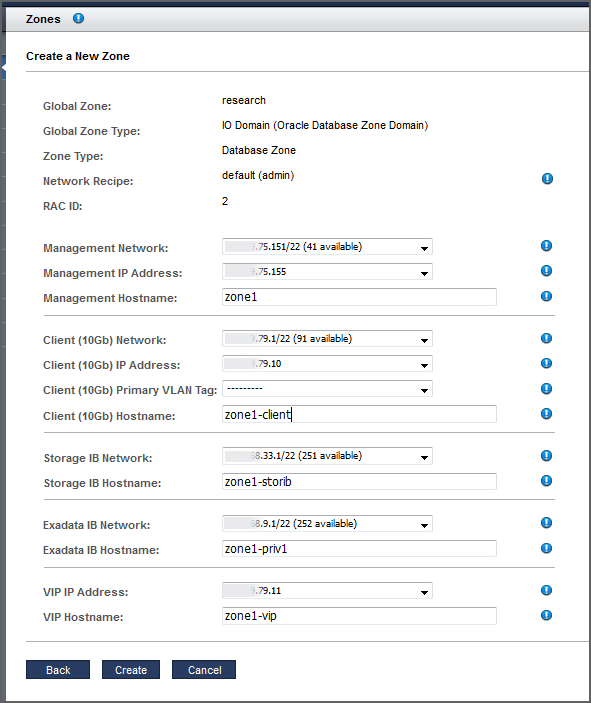
Management Network – You can select the Management Network from which to assign an IP Address. All Management Networks defined in the Added Network Resources table of the Network Resources page with sufficient free IP Addresses can be selected. If the Resource Recipe for the I/O Domain that you are configuring contains two Management Interfaces, you will see two sets of inputs in order to provide two entries for the Management Network, IP Address, VLAN Tag, and Hostname. In this case, two Management interfaces will be configured in the I/O Domain after it has been deployed. If the I/O Domain has two Management Interfaces, then each of those Management Interfaces can use any Management Network with sufficient available IP Addresses.
-
Management Hostname – Type a unique name for this zone.
-
Client (10Gb) Network – You can select the Client Network from which to assign an IP Address. All Client Networks defined in the Added Network Resources table of the Network Resources page with sufficient free IP Addresses can be selected. If the Resource Recipe for the I/O Domain that you are configuring contains two Client (10Gb) Interfaces, you will see two sets of inputs in order to provide two entries for the Client Network, IP Address, VLAN Tag, and Hostname. In this case, two Client (10Gb) interfaces will be configured in the I/O Domain after it has been deployed. If an I/O Domain has two Client Interfaces, then each of those Client Interfaces can use any Client Network with sufficient available IP Addresses.
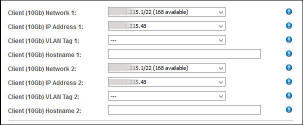
For more information, see Add VLAN Tags (Administrators).
-
Client (10Gb) IP Address – Displayed only if the IP Address assignment is set to manual. See Configure How IP Addresses are Assigned (Administrators). When this setting is enabled, you see a drop-down list of IP Addresses from the selected Client (10Gb) Network and you can select the desired IP Address.
-
Client (10Gb) VLAN Tag – This field is always present on the I/O Domain configuration page, even if you did not define any VLAN tags in the Network Resources section. The default is no VLAN tag, which is indicated by ---.
-
Client (10Gb) Hostname – Use the default, or type a unique name for the client network for this zone.
-
Storage IB Network – Depending how the assistant is configured, the IP address might be automatically assigned or you might be able to choose an available IP address for the ZFS Storage Network for this zone. See Configure How IP Addresses are Assigned (Administrators).
-
Storage IB Hostname – Use the default, or type a unique name for the ZFS storage hostname for this zone.
-
Exadata IB Network – Depending how the assistant is configured (see Configure How IP Addresses are Assigned (Administrators)), the IP address might be automatically assigned or you might be able to choose an available IP address for the Exadata network for this zone.
-
Exadata IB Hostname – Use the default, or type a unique name to the Exadata host name for this zone.
-
VIP Hostname – Use the default, or type a unique name for the virtual IP network hostname for this zone.
For example:
-
-
Click Create to configure a new zone.
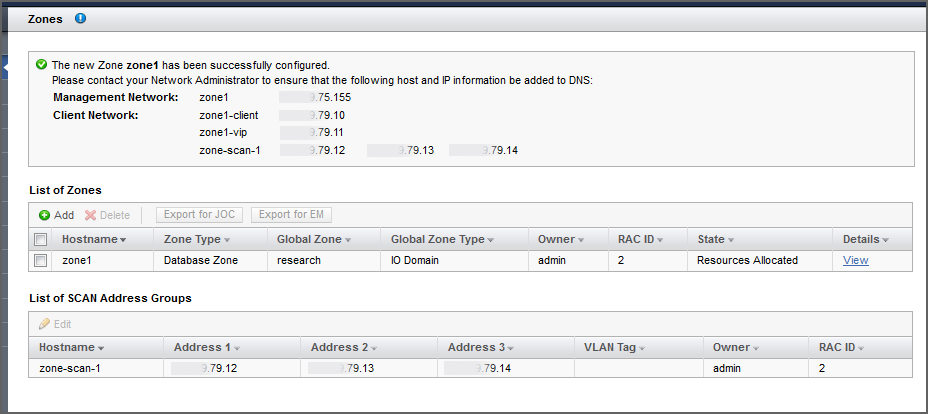
The Zones screen appears again, with a list of configured zones and configured SCAN Address Groups. A note at the top of this screen provides DNS information for the new zone that you just configured. This example shows two Database Zones that are part of a single RAC.
-
Add the management and client networks to DNS.
The network host names and IP addresses are displayed in the confirmation panel in the Zones screen, and available when you view the zone's details.
-
Consider your next action.
-
Configure additional zones for RAC – See Configure a Database Zone.
-
Install the Oracle Database on the database zones that you just configured – See Preparing to Configure a Database on a Database Domain or Database Zone.
-
Export zone information to Oracle Enterprise Manager – See Export a Zones Text File to Oracle Enterprise Manager.
-
Remove a zone's configuration information – See Delete Zone Configuration Information.
-